Anti-IKKα Antibody (2115)
$445.00
SKU: 2115
Categories: Antibody Products, Neuroscience and Signal Transduction Antibodies, Products
Overview
Product Name Anti-IKKα Antibody (2115)
Description Anti-IKKα Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Target IKKα
Species Reactivity Human
Applications ELISA,WB,ICC,IF
Host Rabbit
Clonality Polyclonal
Isotype IgG
Immunogen Peptide corresponding to aa 699-715 of human IKKa which differs from the corresponding murine sequence by one amino acid.
Properties
Form Liquid
Concentration Lot Specific
Formulation PBS, pH 7.4.
Buffer Formulation Phosphate Buffered Saline
Buffer pH pH 7.4
Format Purified
Purification Purified by peptide immuno-affinity chromatography
Specificity Information
Specificity This antibody recognizes human IKKalpha (85 kD). No cross-reactivity with IKKb or IKKg.
Target Name Inhibitor of nuclear factor κ-B kinase subunitα
Target ID IKKα
Uniprot ID O15111
Alternative Names I-κ-B kinaseα, IKK-A, IKK-α, IkBKA, IκB kinase, EC 2.7.11.10, Conserved helix-loop-helix ubiquitous kinase, I-κ-B kinase 1, IKK1, Nuclear factor NF-κ-B inhibitor kinaseα, NFKBIKA, Transcription factor 16, TCF-16
Gene Name CHUK
Gene ID 1147
Accession Number NP_001269
Sequence Location Cytoplasm, Nucleus
Biological Function Serine kinase that plays an essential role in the NF-kappa-B signaling pathway which is activated by multiple stimuli such as inflammatory cytokines, bacterial or viral products, DNA damages or other cellular stresses (PubMed:9244310, PubMed:9252186, PubMed:9346484, PubMed:18626576). Acts as part of the canonical IKK complex in the conventional pathway of NF-kappa-B activation and phosphorylates inhibitors of NF-kappa-B on serine residues (PubMed:9244310, PubMed:9252186, PubMed:9346484, PubMed:18626576). These modifications allow polyubiquitination of the inhibitors and subsequent degradation by the proteasome (PubMed:9244310, PubMed:9252186, PubMed:9346484, PubMed:18626576). In turn, free NF-kappa-B is translocated into the nucleus and activates the transcription of hundreds of genes involved in immune response, growth control, or protection against apoptosis (PubMed:9244310, PubMed:9252186, PubMed:9346484, PubMed:18626576). Negatively regulates the pathway by phosphorylating the scaffold protein TAXBP1 and thus promoting the assembly of the A20/TNFAIP3 ubiquitin-editing complex (composed of A20/TNFAIP3, TAX1BP1, and the E3 ligases ITCH and RNF11) (PubMed:21765415). Therefore, CHUK plays a key role in the negative feedback of NF-kappa-B canonical signaling to limit inflammatory gene activation. As part of the non-canonical pathway of NF-kappa-B activation, the MAP3K14-activated CHUK/IKKA homodimer phosphorylates NFKB2/p100 associated with RelB, inducing its proteolytic processing to NFKB2/p52 and the formation of NF-kappa-B RelB-p52 complexes (PubMed:20501937). In turn, these complexes regulate genes encoding molecules involved in B-cell survival and lymphoid organogenesis. Participates also in the negative feedback of the non-canonical NF-kappa-B signaling pathway by phosphorylating and destabilizing MAP3K14/NIK. Within the nucleus, phosphorylates CREBBP and consequently increases both its transcriptional and histone acetyltransferase activities (PubMed:17434128). Modulates chromatin accessibility at NF-kappa-B-responsive promoters by phosphorylating histones H3 at 'Ser-10' that are subsequently acetylated at 'Lys-14' by CREBBP (PubMed:12789342). Additionally, phosphorylates the CREBBP-interacting protein NCOA3. Also phosphorylates FOXO3 and may regulate this pro-apoptotic transcription factor (PubMed:15084260). Phosphorylates RIPK1 at 'Ser-25' which represses its kinase activity and consequently prevents TNF-mediated RIPK1-dependent cell death (By similarity). Phosphorylates AMBRA1 following mitophagy induction, promoting AMBRA1 interaction with ATG8 family proteins and its mitophagic activity (PubMed:30217973). {UniProtKB:Q60680, PubMed:12789342, PubMed:15084260, PubMed:17434128, PubMed:20434986, PubMed:20501937, PubMed:21765415, PubMed:30217973, PubMed:9244310, PubMed:9252186, PubMed:9346484, PubMed:18626576}.
Research Areas Neuroscience
Background Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) is a ubiquitous transcription factor and key mediator of gene expression during immune and inflammatory responses. NF-kappaB activates numerous genes in response to extracellular stimuli, such as IL-1, TNFalpha, and LPS. NF-kappaB is associated with IkappaB in cytoplasm, which inhibits NF-kappaB activity. IkappaB kinase (IKK), which phosphorylates IkappaB and mediates IkappaB degradation and NF-kappaB activation, was recently identified. IKK is a serine protein kinase, and the IKK complex contains alpha and beta subunits (IKKalpha and IKKbeta). IKKalpha and IKKbeta interact with each other, and both are essential for NF-B activation. IKKalpha specifically phosphorylates IkappaB-alpha and is expressed in a variety of human tissues.
Application Images




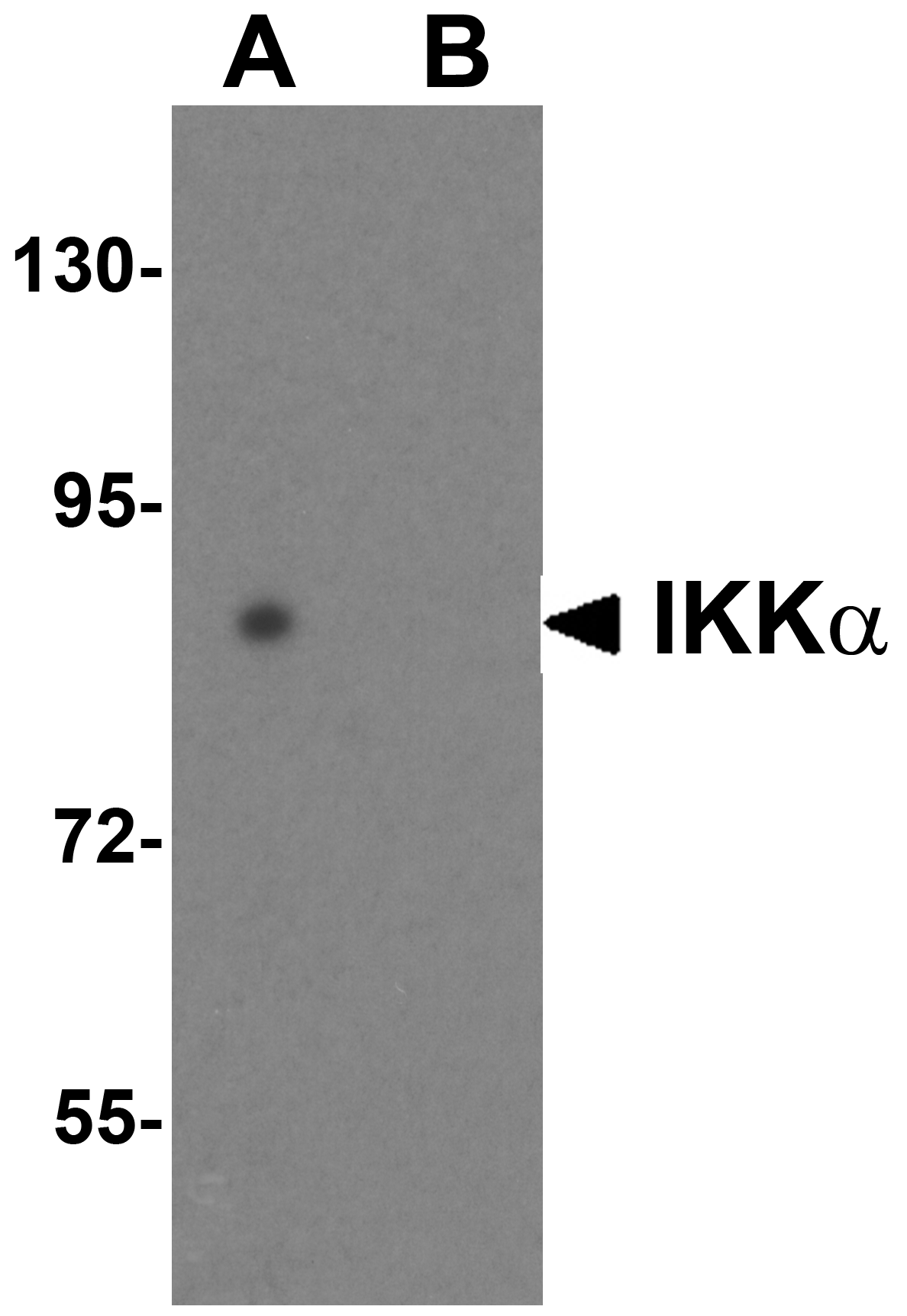
Description Western blot analysis of IKK alpha in HeLa cell lysate with IKK alpha antibody at 1 ug/mL in (A) the absence and (B) the presence of blocking peptide.

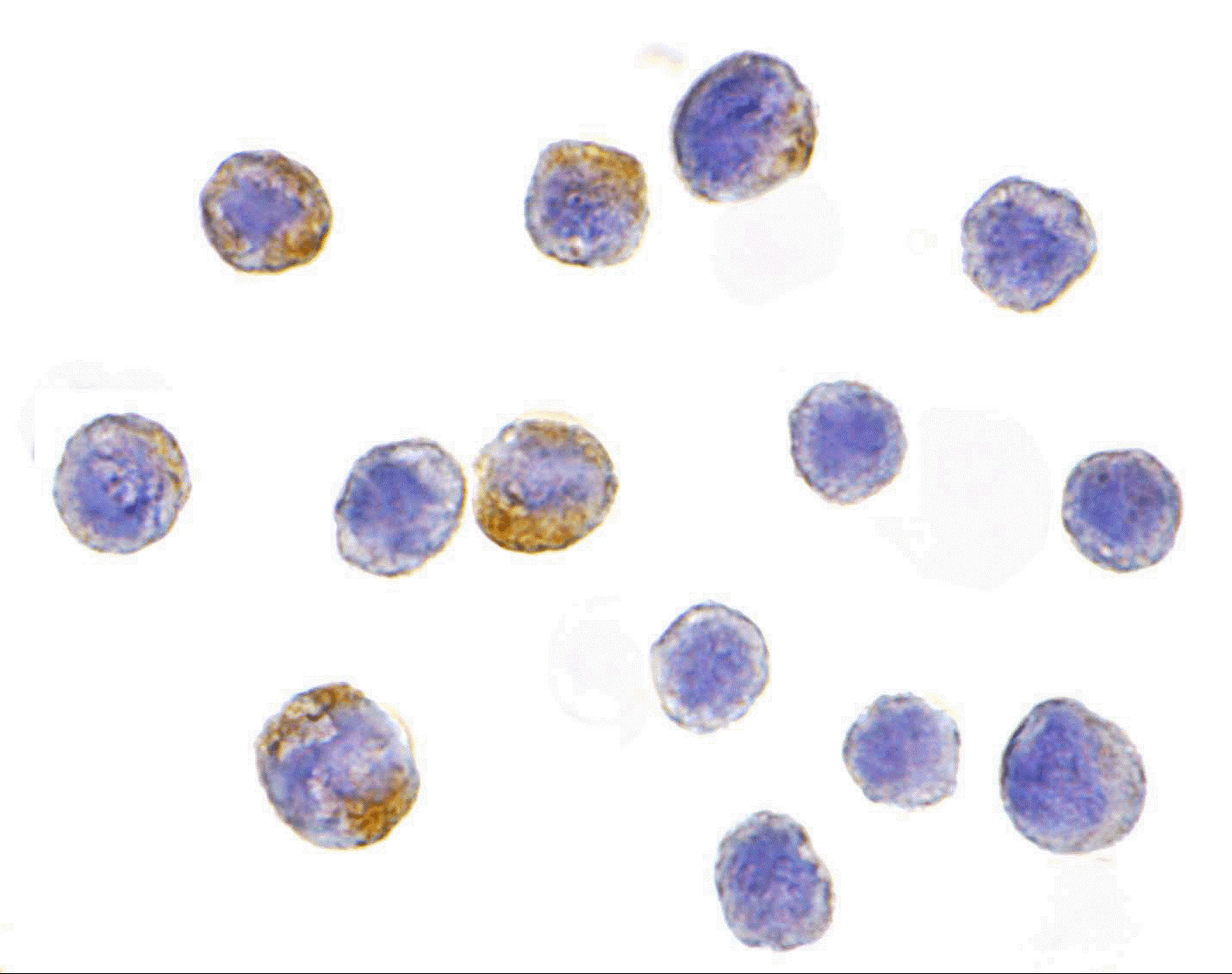
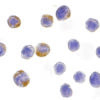
Description Immunocytochemistry of IKK alpha in HeLa cells with IKK alpha antibody at 10 ug/mL.

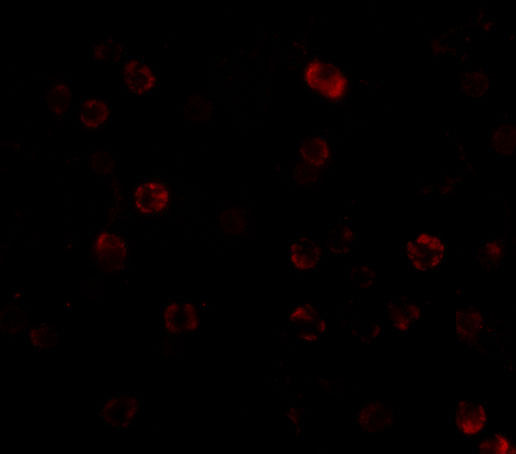
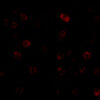
Description Immunofluorescence of IKKa in HeLa cells with IKKa antibody at 2 ug/mL.
Handling
Storage This antibody is stable for at least one (1) year at -20°C. Avoid multiple freeze- thaw cycles.
Dilution Instructions Dilute in PBS or medium which is identical to that used in the assay system.
Application Instructions Immunoblotting: use at 1:500-1:1,000 dilution.
Positive control: Whole cell lysate from HeLa or Jurkat cells.
Positive control: Whole cell lysate from HeLa or Jurkat cells.
References & Data Sheet
Data Sheet  Download PDF Data Sheet
Download PDF Data Sheet
 Download PDF Data Sheet
Download PDF Data Sheet