Anti-E-Cadherin Antibody (34060)
$208.00
Overview
Product Name Anti-E-Cadherin Antibody (34060)
Description Anti-E-cadherin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
Target E-Cadherin
Species Reactivity Human
Applications IHC
Host Mouse
Clonality Monoclonal
Clone ID G564.1
Isotype IgG1
Immunogen Recombinant human E-cadherin.
Properties
Form Liquid
Concentration Lot Specific
Formulation Tris buffer, pH 7.3-7.7, 1% BSA, 0.1% sodium azide.
Buffer Formulation Tris
Buffer pH pH 7.3-7.7
Buffer Anti-Microbial 0.1% Sodium Azide
Buffer Protein Stabilizer 1% Bovine Serum Albumin
Format Purified
Purification Purified by immunoaffinity chromatography
Specificity Information
Specificity Human E-cadherin. Reactivity with other species has not been investigated.
Target Name Cadherin-1
Target ID E-Cadherin
Uniprot ID P12830
Alternative Names CAM 120/80, Epithelial cadherin, E-cadherin, Uvomorulin, CD antigen CD324 [Cleaved into: E-Cad/CTF1; E-Cad/CTF2; E-Cad/CTF3]
Gene Name CDH1
Sequence Location Cell junction, adherens junction, Cell membrane, Single-pass type I membrane protein. Endosome. Golgi apparatus, trans-Golgi network. Note=Colocalizes with DLGAP5 at sites of cell-cell contact in intestinal epithelial cells. Anchored to actin microfilaments through association with α-, beta- and γ-catenin. Sequential proteolysis induced by apoptosis or calcium influx, results in translocation from sites of cell-cell contact to the cytoplasm. Colocalizes with RAB11A endosomes during its transport from the Golgi apparatus to the plasma membrane.
Biological Function Cadherins are calcium-dependent cell adhesion proteins (PubMed:11976333). They preferentially interact with themselves in a homophilic manner in connecting cells; cadherins may thus contribute to the sorting of heterogeneous cell types. CDH1 is involved in mechanisms regulating cell-cell adhesions, mobility and proliferation of epithelial cells (PubMed:11976333). Has a potent invasive suppressor role. It is a ligand for integrin alpha-E/beta-7. {PubMed:11976333, PubMed:16417575}.; E-Cad/CTF2 promotes non-amyloidogenic degradation of Abeta precursors. Has a strong inhibitory effect on APP C99 and C83 production. {PubMed:16417575}.; (Microbial infection) Serves as a receptor for Listeria monocytogenes; internalin A (InlA) binds to this protein and promotes uptake of the bacteria. {PubMed:10406800, PubMed:17540170, PubMed:8601315}.
Research Areas Cancer research
Background E-cadherin is a calcium-dependent intercellular adhesion molecule encoded by the CDH1 gene and present on epithelial cells. Loss of E-cadherin function or expression has been implicated in cancer progression and metastasis. E-cadherin downregulation decreases the strength of cellular adhesion within a tissue, resulting in an increase in cellular motility. This may allow cancer cells to cross the basement membrane and invade surrounding tissues. E-cadherin is also used by pathologists to diagnose different kinds of breast cancer. When compared with invasive ductal carcinoma, E-cadherin expression is markedly reduced or absent in the great majority of invasive lobular carcinomas when studied by immunohistochemistry.
Application Images


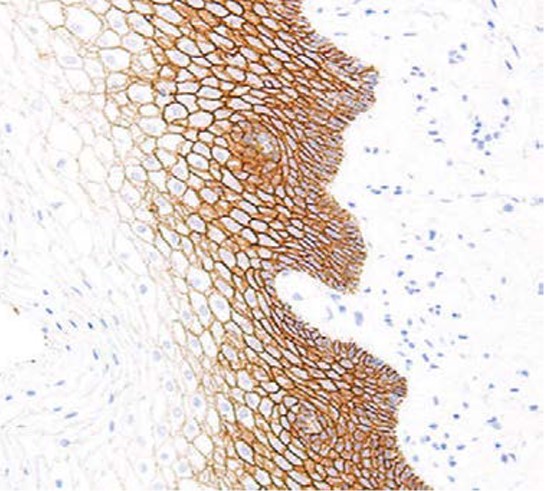
Description Immunohistochemistry: use at a dilution of 1:100-1:200 on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded samples after heat-induced epitope retrieval at pH 9 for 10-30 minutes. Detection of E-cadherin in human breast with #34060 diluted 1:100-1:200.
Handling
Storage Store at 2-8°C. Do not freeze.
Dilution Instructions Dilute in PBS or medium that is identical to that used in the assay system.
Application Instructions
Immunohistochemistry: use at a dilution of 1:100-1:200 on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded samples after heat-induced epitope retrieval at pH 9 for 10-30 minutes.
Immunohistochemistry: use at a dilution of 1:100-1:200 on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded samples after heat-induced epitope retrieval at pH 9 for 10-30 minutes.
References & Data Sheet
Data Sheet  Download PDF Data Sheet
Download PDF Data Sheet
 Download PDF Data Sheet
Download PDF Data Sheet