Anti-NAK/TBK1 (CT) Antibody (56114)
$445.00
| Host | Quantity | Applications | Species Reactivity | Data Sheet | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rabbit | 100ug | ELISA,WB,ICC | Human, Mouse, Rat |  |
SKU: 56114
Categories: Antibody Products, Neuroscience and Signal Transduction Antibodies, Products
Overview
Product Name Anti-NAK/TBK1 (CT) Antibody (56114)
Description Anti-NAK/TBK1 (CT) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Target NAK/TBK1 (CT)
Species Reactivity Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications ELISA,WB,ICC
Host Rabbit
Clonality Polyclonal
Immunogen Peptide corresponding to aa 712-727 of human NAK/TBK1. This sequence is identical to that of mouse NAK/TBK1.
Properties
Form Liquid
Concentration Lot Specific
Formulation PBS, pH 7.4.
Buffer Formulation Phosphate Buffered Saline
Buffer pH pH 7.4
Format Purified
Purification Purified by peptide immuno-affinity chromatography
Specificity Information
Specificity This antibody recognizes an epitope at the C-terminus of human, mouse, and rat NAK/TBK1 (NF-kappaB Activating Kinase and TANK-Binding Kinase 1). NAK/TBK1 activates IKKb through direct phosphorylation and activates NF-kappaB as well in response to growth factors. NAK/TBK1 functions upstream of NIK and the IKK complex and is critical in protecting embryonic liver from apoptosis. This antibody does not cross-react with IKKalpha, IKKb, IKKepsilon, or IKKg.
Target Name Serine/threonine-protein kinase TBK1
Target ID NAK/TBK1 (CT)
Uniprot ID Q9UHD2
Alternative Names EC 2.7.11.1, NF-κ-B-activating kinase, T2K, TANK-binding kinase 1
Gene Name TBK1
Sequence Location Cytoplasm
Biological Function Serine/threonine kinase that plays an essential role in regulating inflammatory responses to foreign agents (PubMed:12692549, PubMed:14703513, PubMed:18583960, PubMed:12702806, PubMed:15367631, PubMed:10581243, PubMed:11839743, PubMed:15485837, PubMed:21138416, PubMed:25636800, PubMed:23453971, PubMed:23453972, PubMed:23746807, PubMed:26611359, PubMed:32404352). Following activation of toll-like receptors by viral or bacterial components, associates with TRAF3 and TANK and phosphorylates interferon regulatory factors (IRFs) IRF3 and IRF7 as well as DDX3X (PubMed:12692549, PubMed:14703513, PubMed:18583960, PubMed:12702806, PubMed:15367631, PubMed:25636800). This activity allows subsequent homodimerization and nuclear translocation of the IRFs leading to transcriptional activation of pro-inflammatory and antiviral genes including IFNA and IFNB (PubMed:12702806, PubMed:15367631, PubMed:25636800, PubMed:32972995). In order to establish such an antiviral state, TBK1 form several different complexes whose composition depends on the type of cell and cellular stimuli (PubMed:23453971, PubMed:23453972, PubMed:23746807). Plays a key role in IRF3 activation: acts by first phosphorylating innate adapter proteins MAVS, STING1 and TICAM1 on their pLxIS motif, leading to recruitment of IRF3, thereby licensing IRF3 for phosphorylation by TBK1 (PubMed:25636800, PubMed:30842653). Phosphorylated IRF3 dissociates from the adapter proteins, dimerizes, and then enters the nucleus to induce expression of interferons (PubMed:25636800). Thus, several scaffolding molecules including FADD, TRADD, MAVS, AZI2, TANK or TBKBP1/SINTBAD can be recruited to the TBK1-containing-complexes (PubMed:21931631). Under particular conditions, functions as a NF-kappa-B effector by phosphorylating NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha/NFKBIA, IKBKB or RELA to translocate NF-Kappa-B to the nucleus (PubMed:10783893, PubMed:15489227). Restricts bacterial proliferation by phosphorylating the autophagy receptor OPTN/Optineurin on 'Ser-177', thus enhancing LC3 binding affinity and antibacterial autophagy (PubMed:21617041). Phosphorylates SMCR8 component of the C9orf72-SMCR8 complex, promoting autophagosome maturation (PubMed:27103069). Phosphorylates ATG8 proteins MAP1LC3C and GABARAPL2, thereby preventing their delipidation and premature removal from nascent autophagosomes (PubMed:31709703). Phosphorylates and activates AKT1 (PubMed:21464307). Seems to play a role in energy balance regulation by sustaining a state of chronic, low-grade inflammation in obesity, wich leads to a negative impact on insulin sensitivity (By similarity). Attenuates retroviral budding by phosphorylating the endosomal sorting complex required for transport-I (ESCRT-I) subunit VPS37C (PubMed:21270402). Phosphorylates Borna disease virus (BDV) P protein (PubMed:16155125). Plays an essential role in the TLR3- and IFN-dependent control of herpes virus HSV-1 and HSV-2 infections in the central nervous system (PubMed:22851595). {UniProtKB:Q9WUN2, PubMed:10581243, PubMed:10783893, PubMed:11839743, PubMed:12692549, PubMed:12702806, PubMed:14703513, PubMed:15367631, PubMed:15485837, PubMed:15489227, PubMed:16155125, PubMed:18583960, PubMed:21138416, PubMed:21270402, PubMed:21464307, PubMed:21617041, PubMed:21931631, PubMed:22851595, PubMed:23453971, PubMed:23453972, PubMed:23746807, PubMed:25636800, PubMed:26611359, PubMed:27103069, PubMed:30842653, PubMed:31709703, PubMed:32972995}.
Research Areas Neuroscience
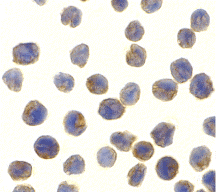
Application Images


Description Immunocytochemistry of NAK in MOLT4 cells with NAK antibody at 10 ug/mL.
Handling
Storage This antibody is stable for at least one (1) year at -20°C. Avoid multiple freeze- thaw cycles.
Dilution Instructions Dilute in PBS or medium which is identical to that used in the assay system.
Application Instructions Immunoblotting: use at 0.5-1 ug/mL. In immunoblots, a band of 84 kD is detected.
Positive control: MOLT4 cell lysate.
Positive control: MOLT4 cell lysate.
References & Data Sheet
Data Sheet  Download PDF Data Sheet
Download PDF Data Sheet
 Download PDF Data Sheet
Download PDF Data Sheet