Anti-Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1 (FGFR1) Antibody (30102)
$614.00
SKU: 30102
Categories: Antibody Products, Growth Factors/Cytokines/Receptor Antibodies, Products
Overview
Product Name Anti-Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1 (FGFR1) Antibody (30102)
Description Anti-FGF Receptor 1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
Target Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1 (FGFR1)
Species Reactivity Human
Applications WB,IHC,IP
Host Mouse
Clonality Monoclonal
Clone ID M5G10
Isotype IgG1
Immunogen Recombinant human ectodomain of FGFR-1b expressed in E. coli beginning with proline 23; antigen contained NH2-terminal gly-ser-pro-gly-ile and COOH-terminal glu-phe sequences.
Properties
Form Liquid
Concentration Lot Specific
Formulation PBS, pH 7.4
Buffer Formulation Phosphate Buffered Saline
Buffer pH pH 7.4
Format Purified
Purification Purified by Protein G affinity chromatography
Specificity Information
Specificity This antibody reacts with both alpha (denatured) and b isoforms. Epitope is within the sequence his241 and val267 between Ig loops II and III. Epitope is masked in undenatured FGFr1alpha.
Target Name Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1
Target ID Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1 (FGFR1)
Uniprot ID P11362
Alternative Names FGFR-1, EC 2.7.10.1, Basic fibroblast growth factor receptor 1, BFGFR, bFGF-R-1, Fms-like tyrosine kinase 2, FLT-2, N-sam, Proto-oncogene c-Fgr, CD antigen CD331
Gene Name FGFR1
Sequence Location Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Nucleus. Cytoplasm, cytosol. Cytoplasmic vesicle. Note=After ligand binding, both receptor and ligand are rapidly internalized. Can translocate to the nucleus after internalization, or by translocation from the endoplasmic reticulum or Golgi apparatus to the cytosol, and from there to the nucleus.
Biological Function Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as cell-surface receptor for fibroblast growth factors and plays an essential role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, differentiation and migration. Required for normal mesoderm patterning and correct axial organization during embryonic development, normal skeletogenesis and normal development of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) neuronal system. Phosphorylates PLCG1, FRS2, GAB1 and SHB. Ligand binding leads to the activation of several signaling cascades. Activation of PLCG1 leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Phosphorylation of FRS2 triggers recruitment of GRB2, GAB1, PIK3R1 and SOS1, and mediates activation of RAS, MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 and the MAP kinase signaling pathway, as well as of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Promotes phosphorylation of SHC1, STAT1 and PTPN11/SHP2. In the nucleus, enhances RPS6KA1 and CREB1 activity and contributes to the regulation of transcription. FGFR1 signaling is down-regulated by IL17RD/SEF, and by FGFR1 ubiquitination, internalization and degradation. {UniProtKB:P16092, PubMed:10830168, PubMed:11353842, PubMed:12181353, PubMed:1379697, PubMed:1379698, PubMed:15117958, PubMed:16597617, PubMed:17311277, PubMed:17623664, PubMed:18480409, PubMed:19224897, PubMed:19261810, PubMed:19665973, PubMed:20133753, PubMed:20139426, PubMed:21765395, PubMed:8622701, PubMed:8663044}.
Research Areas Growth Factors, Cytokines, Receptors
Background The fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family is a group of multi-functional polypeptides that function in embryonic development, tissue repair, neuronal cell survival, cardiovascular disease, and tumorigenesis. The biological activities of FGF are mediated by cell surface receptors that have tyrosine kinase activity. FGFR-1 is activated by FGF-1 and FGF-2. In neoplastic cells, overexpression of FGF-1, FGF-2 and FGF receptors appear to contribute to cellular trans- formation and proliferation.
Application Images




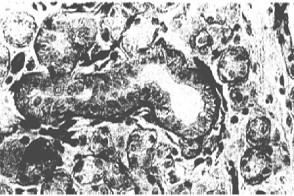
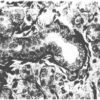
Description Immunohistochemistry: 10ug/ml, paraffin- embedded tissue. Detection of FGFR-1 in normal salivary gland.

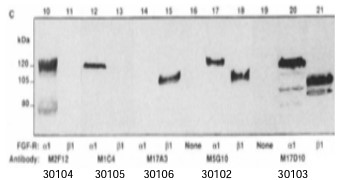
Description Immunoblotting:1ug/ml recognizes 10ng recombinant bacterial, baculoviral or native FGFR1. 30104 3010530106 30102 30103 Detection of α and β isoforms in recombinant FGFR-1 expressed in Sf9 cells by #30102 alongwith other QED Bioscience FGFR-1 MAbs.

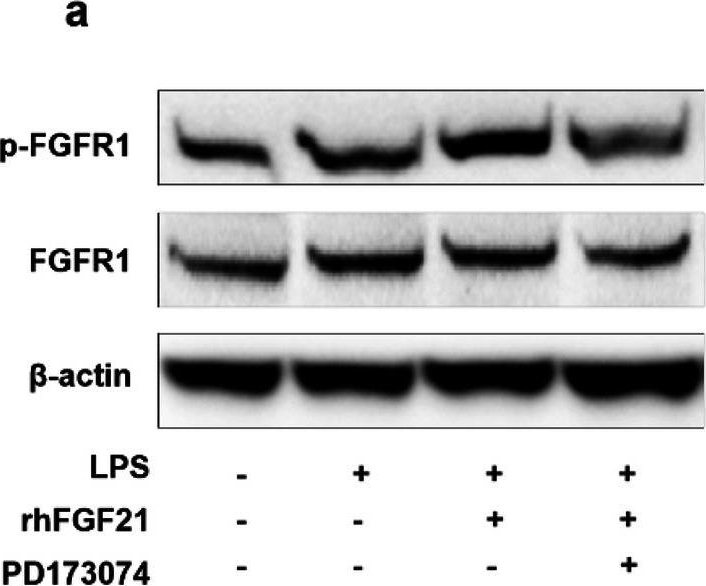
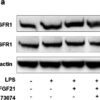
Description Effects of rhFGF21 on PPAR-γ and NF-κB signaling in LPS-stimulated BV2 cell line. a Representative band of p-FGFR1 and FGFR1 by western blot assay based on an internal control of Beta-actin and quantitated in the graph (c). b Amount of NF-κB and PPAR-γ in the nucleus of the control with H3 and quantitated in the graph (d NF-κB and e PPAR-γ). n = 4 per group. Values are mean ± SEM by one-way ANOVA
Handling
Storage These antibodies are stable for at least one (1) year at -20°C to -70°C. Store product in appropriate aliquots to avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles.
Dilution Instructions Dilute in PBS or medium that is identical to that used in the assay system.
Application Instructions
Immunohistochemistry: 10ug/ml, paraffin- embedded tissue.
Immunoblotting: 1ug/ml recognizes 10ng recombinant bacterial, baculoviral or native FGFR1.
Immunoprecipitation: native, recombinant, and ligand-labeled FGFr1.
Immunohistochemistry: 10ug/ml, paraffin- embedded tissue.
Immunoblotting: 1ug/ml recognizes 10ng recombinant bacterial, baculoviral or native FGFR1.
Immunoprecipitation: native, recombinant, and ligand-labeled FGFr1.
References & Data Sheet
References Xu et al. (1992) J Biol Chem 267: 17792
Wang et al. (1995) J Biol Chem 270: 10231
Myoken et al. (1996) J Pathol 178: 429
Kong, S., Cao, Y. (2020), et al. Cell Mol Med. 24(8):4677-4686
FGF21 alleviates neuroinflammation following ischemic stroke by modulating the temporal and spatial dynamics of microglia/macrophages. J Neuroinflammation (2020) [32867781]
Wang et al. (1995) J Biol Chem 270: 10231
Myoken et al. (1996) J Pathol 178: 429
Kong, S., Cao, Y. (2020), et al. Cell Mol Med. 24(8):4677-4686
FGF21 alleviates neuroinflammation following ischemic stroke by modulating the temporal and spatial dynamics of microglia/macrophages. J Neuroinflammation (2020) [32867781]
Data Sheet  Download PDF Data Sheet
Download PDF Data Sheet
 Download PDF Data Sheet
Download PDF Data Sheet