Anti-APP (Aβ-NT) Antibody (2133)
$445.00
| Host | Quantity | Applications | Species Reactivity | Data Sheet | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rabbit | 100ug | ELISA,WB,IHC-P | Human, Mouse, Rat |  |
SKU: 2133
Categories: Antibody Products, Neuroscience and Signal Transduction Antibodies, Products
Overview
Product Name Anti-APP (Aβ-NT) Antibody (2133)
Description Anti-APP (Aβ-NT) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Target APP (Aβ-NT)
Species Reactivity Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications ELISA,WB,IHC-P
Host Rabbit
Clonality Polyclonal
Isotype IgG
Immunogen Peptide corresponding to aa 653- 662 of human amyloid protein precursor (APP) or aa 1-10 of the 4kD Ab peptide generated by b- and g-secretases. The sequences are identical to those of rabbit, pig, cow, guinea pig, and chicken.
Properties
Form Liquid
Concentration Lot Specific
Formulation PBS, pH 7.4.
Buffer Formulation Phosphate Buffered Saline
Buffer pH pH 7.4
Format Purified
Purification Purified by immunoaffinity chromatography
Specificity Information
Specificity Peptide corresponding to aa 653- 662 of human amyloid protein precursor (APP) or aa 1-10 of the 4kD Ab peptide generated by b- and g-secretases. The sequences are identical to those of rabbit, pig, cow, guinea pig, and chicken.
Target Name Amyloid-β precursor protein
Target ID APP (Aβ-NT)
Uniprot ID P05067
Alternative Names APP, ABPP, APPI, Alzheimer disease amyloid A4 protein homolog, Alzheimer disease amyloid protein, Amyloid precursor protein, Amyloid-β
Gene Name APP
Gene ID 351
Accession Number NP_000475
Sequence Location Cell membrane, Membrane, Perikaryon, Cell projection, growth cone, Membrane, clathrin-coated pit, Early endosome, Cytoplasmic vesicle
Biological Function Functions as a cell surface receptor and performs physiological functions on the surface of neurons relevant to neurite growth, neuronal adhesion and axonogenesis. Interaction between APP molecules on neighboring cells promotes synaptogenesis (PubMed:25122912). Involved in cell mobility and transcription regulation through protein-protein interactions. Can promote transcription activation through binding to APBB1-KAT5 and inhibits Notch signaling through interaction with Numb. Couples to apoptosis-inducing pathways such as those mediated by G(o) and JIP. Inhibits G(o) alpha ATPase activity (By similarity). Acts as a kinesin I membrane receptor, mediating the axonal transport of beta-secretase and presenilin 1 (By similarity). By acting as a kinesin I membrane receptor, plays a role in axonal anterograde transport of cargo towards synapes in axons (PubMed:17062754, PubMed:23011729). Involved in copper homeostasis/oxidative stress through copper ion reduction. In vitro, copper-metallated APP induces neuronal death directly or is potentiated through Cu(2+)-mediated low-density lipoprotein oxidation. Can regulate neurite outgrowth through binding to components of the extracellular matrix such as heparin and collagen I and IV. The splice isoforms that contain the BPTI domain possess protease inhibitor activity. Induces a AGER-dependent pathway that involves activation of p38 MAPK, resulting in internalization of amyloid-beta peptide and leading to mitochondrial dysfunction in cultured cortical neurons. Provides Cu(2+) ions for GPC1 which are required for release of nitric oxide (NO) and subsequent degradation of the heparan sulfate chains on GPC1. {UniProtKB:P12023, PubMed:17062754, PubMed:23011729, PubMed:25122912}.; Amyloid-beta peptides are lipophilic metal chelators with metal-reducing activity. Bind transient metals such as copper, zinc and iron. In vitro, can reduce Cu(2+) and Fe(3+) to Cu(+) and Fe(2+), respectively. Amyloid-beta protein 42 is a more effective reductant than amyloid-beta protein 40. Amyloid-beta peptides bind to lipoproteins and apolipoproteins E and J in the CSF and to HDL particles in plasma, inhibiting metal-catalyzed oxidation of lipoproteins. APP42-beta may activate mononuclear phagocytes in the brain and elicit inflammatory responses. Promotes both tau aggregation and TPK II-mediated phosphorylation. Interaction with overexpressed HADH2 leads to oxidative stress and neurotoxicity. Also binds GPC1 in lipid rafts.; Appicans elicit adhesion of neural cells to the extracellular matrix and may regulate neurite outgrowth in the brain. {ECO:0000250}.; The gamma-CTF peptides as well as the caspase-cleaved peptides, including C31, are potent enhancers of neuronal apoptosis.; N-APP binds TNFRSF21 triggering caspase activation and degeneration of both neuronal cell bodies (via caspase-3) and axons (via caspase-6).
Research Areas Neuroscience
Background Accumulation of the amyloid-beta peptide (Abeta) in the cerebral cortex is a critical event in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. The beta-amyloid protein precursor (APP) is cleaved by beta-secretase, producing a soluble derivative of the protein and a membrane anchored 99-amino acid carboxy-terminal fragment (C99). The C99 fragment serves as substrate for g-secretase to generate the 4 kD amyloid-beta peptide which is deposited in the brain.
Application Images
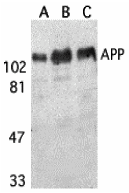


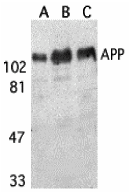
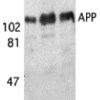
Description Western blot analysis of APP in (A) human, (B) mouse, and (C) rat brain tissue lysates with APP antibody at 1 ug/mL.

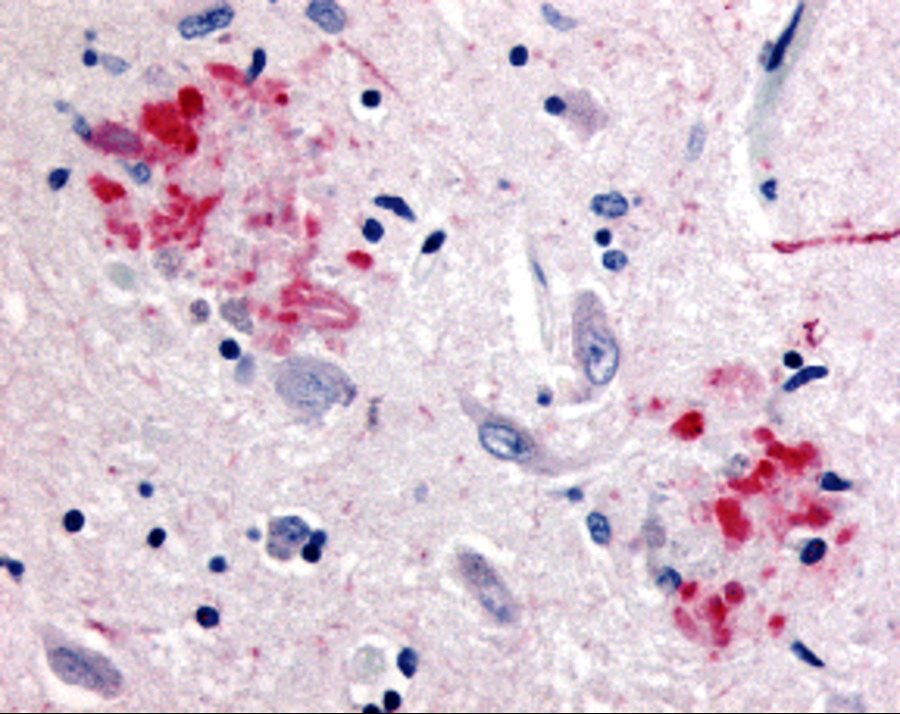
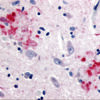
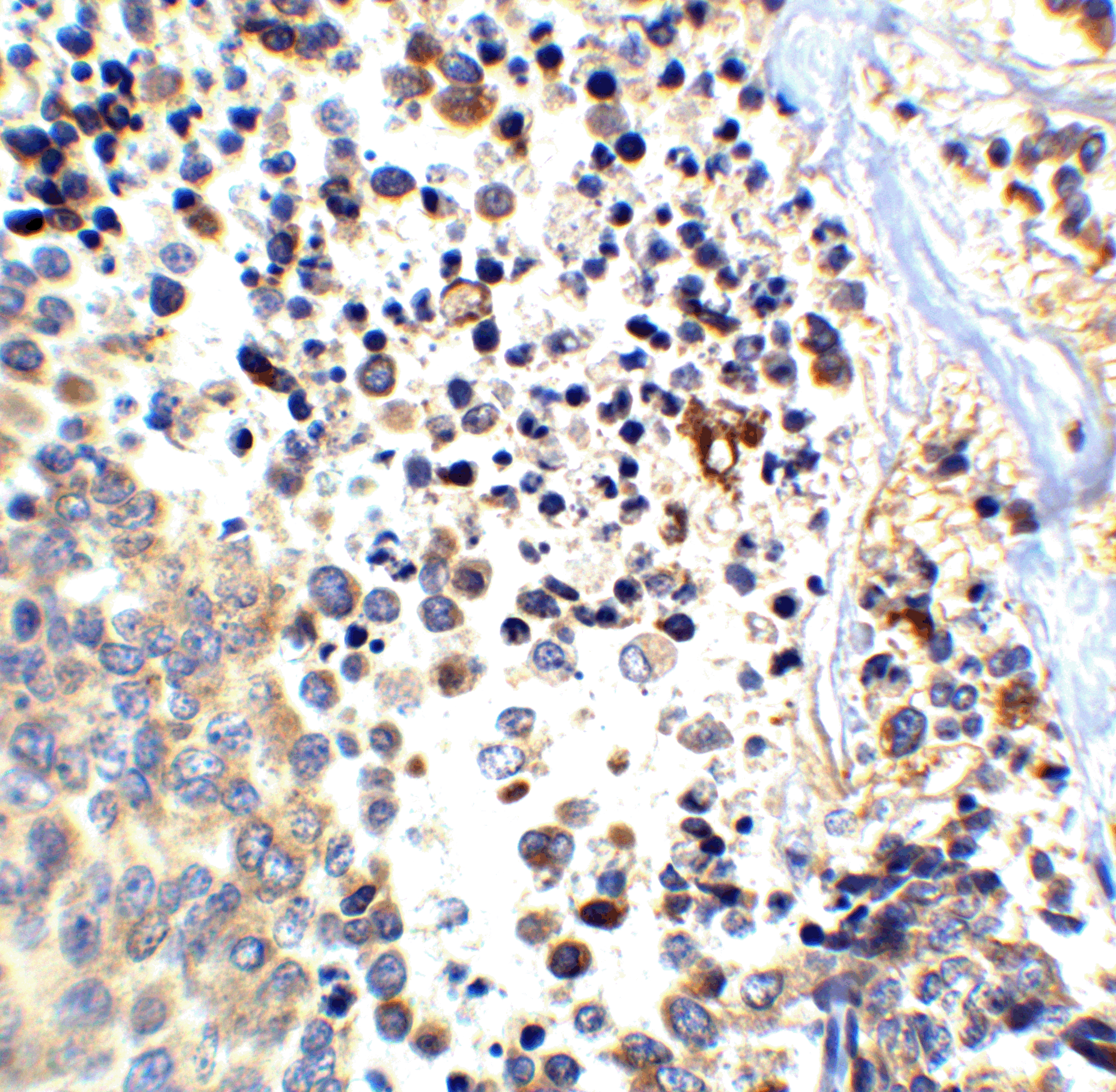
Description Immunohistochemistry of APP in human brain (Alzheimer’s disease) tissue with APP antibody at 10 ug/mL.

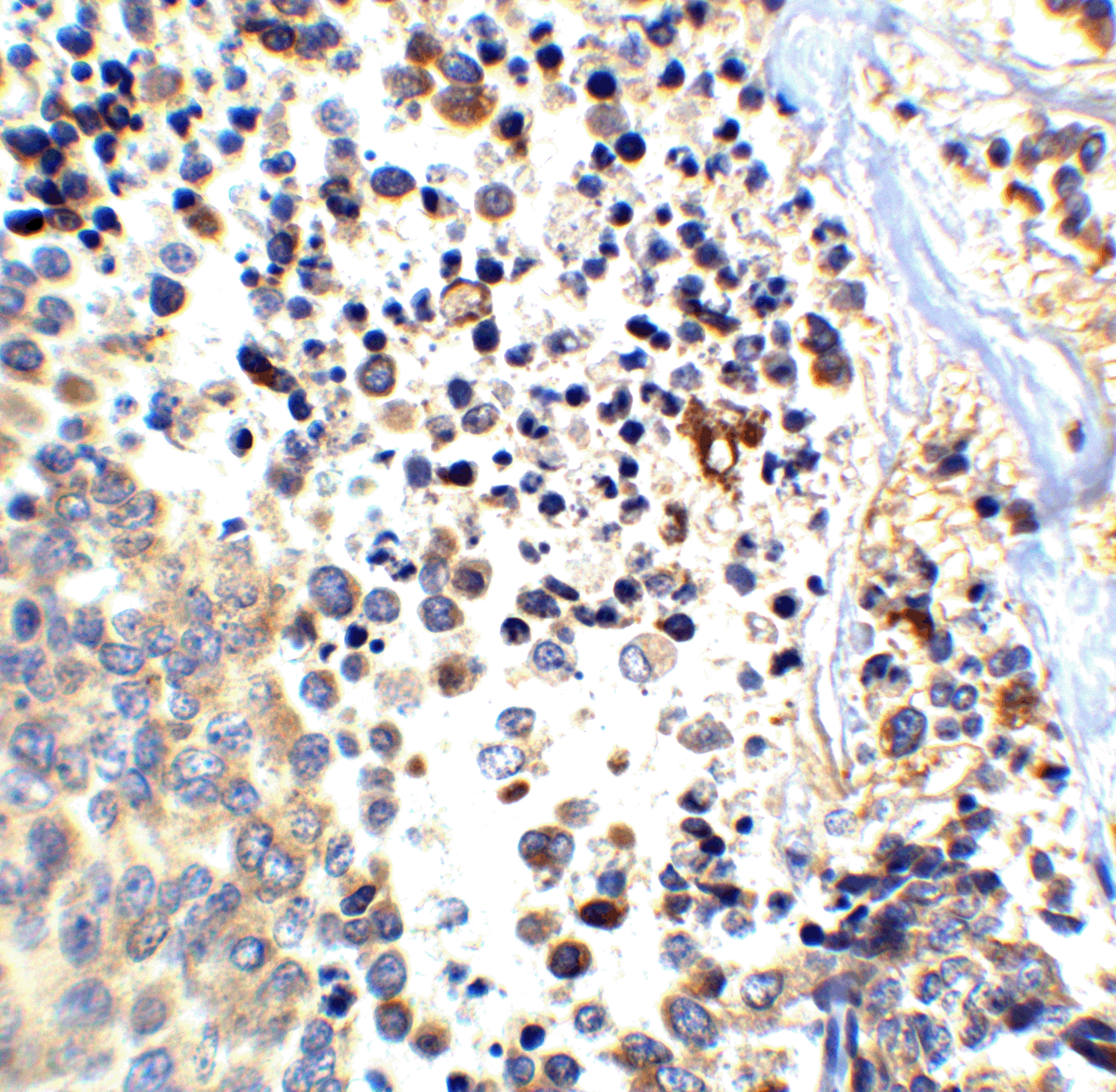
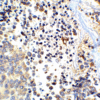
Description Immunohistochemistry of APP in human brain tissue with APP antibody at 2.5 ug/ml.

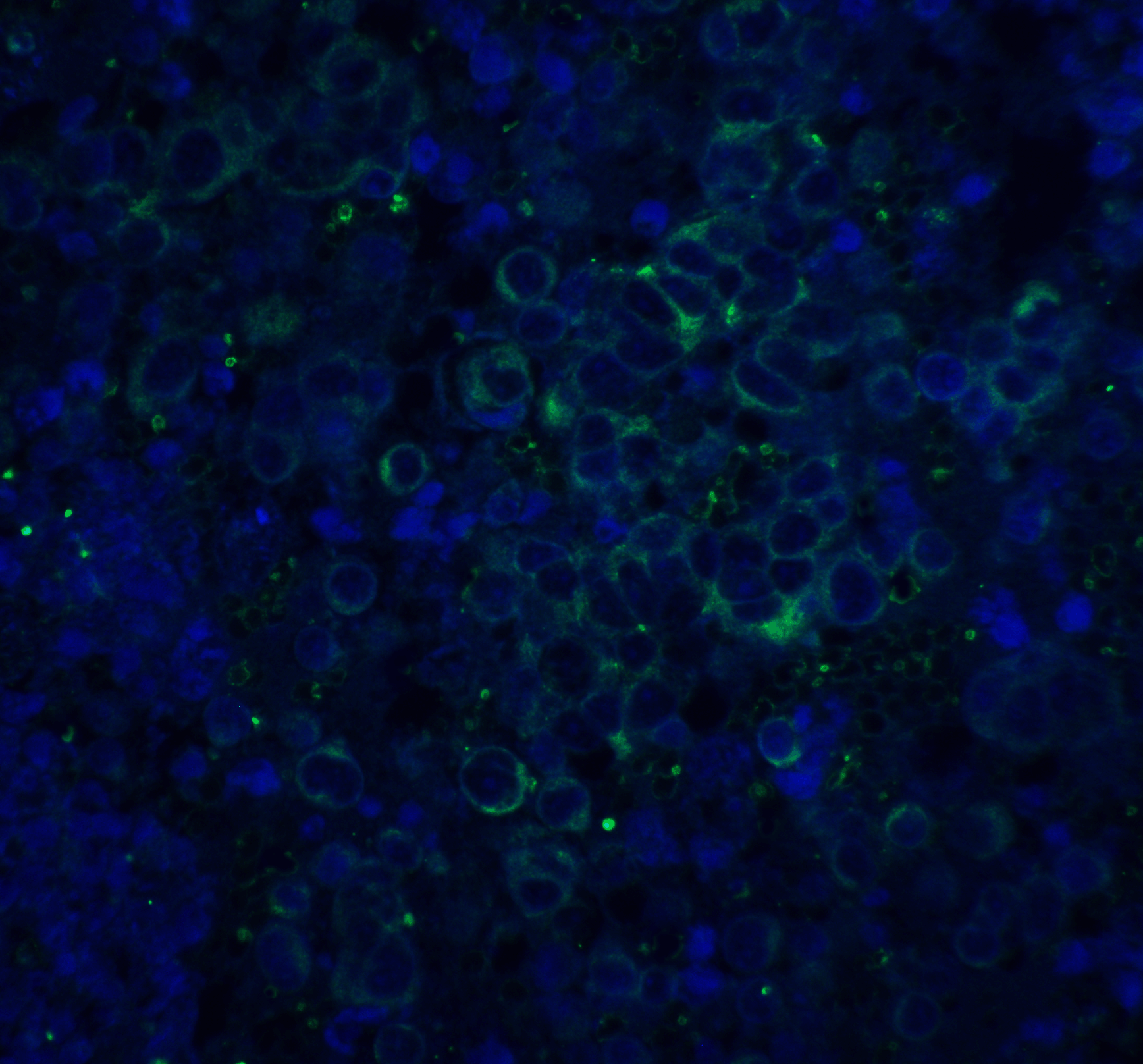
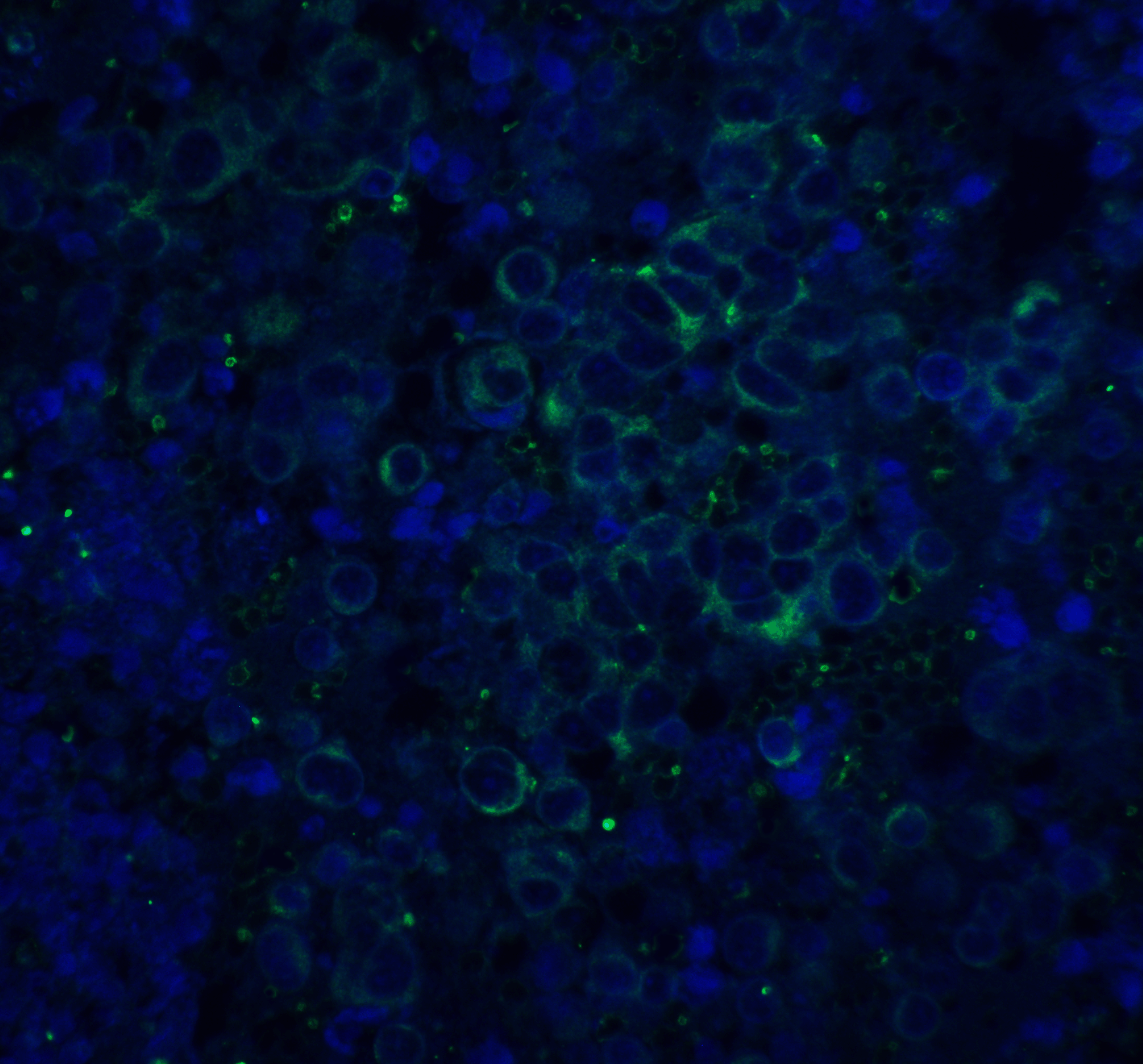
Description Immunofluorescence of ASAH1 in rat heart tissue with ASAH1 antibody at 20 ug/mL.
Green: APP Antibody (2133)
Blue: DAPI staining
Blue: DAPI staining
Handling
Storage This antibody is stable for at least one (1) year at -20°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles.
Dilution Instructions Dilute in PBS or medium which is identical to that used in the assay system.
Application Instructions Immunoblotting: use at 1:500-1:1,000 dilution.
Positive control: Mouse brain lysate.
Positive control: Mouse brain lysate.
References & Data Sheet
Data Sheet  Download PDF Data Sheet
Download PDF Data Sheet
 Download PDF Data Sheet
Download PDF Data Sheet