Anti-DUX4 Antibody (57101)
$390.00
SKU: 57101
Categories: Antibody Products, Neuroscience and Signal Transduction Antibodies, Products
Overview
Product Name Anti-DUX4 Antibody (57101)
Description Anti-DUX4 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
Target DUX4
Species Reactivity Human
Applications IHC,IF
Host Mouse
Clonality Monoclonal
Clone ID P2B1
Isotype IgG1
Immunogen C-terminal 76 amino acids of DUX4 with glutathione-s-transferase (gst) tag.
Properties
Form Liquid
Concentration Lot Specific
Formulation PBS, pH 7.4.
Buffer Formulation Phosphate Buffered Saline
Buffer pH pH 7.4
Format Purified
Purification Purified by Protein G affinity chromatography
Specificity Information
Specificity This antibody recognizes human DUX4. It does not cross-react with DUX4c.
Target Name Double homeobox protein 4
Target ID DUX4
Uniprot ID Q9UBX2
Alternative Names Double homeobox protein 10
Gene Name DUX4
Sequence Location [Isoform 1]: Nucleus
Biological Function [Isoform 1]: Transcription factor that is selectively and transiently expressed in cleavage-stage embryos (PubMed:28459457). Binds to double-stranded DNA elements with the consensus sequence 5'-TAATCTAATCA-3' (PubMed:28459457, PubMed:28459454, PubMed:29572508, PubMed:30540931, PubMed:30315230). Binds to chromatin containing histone H3 acetylated at 'Lys-27' (H3K27ac) and promotes deacetylation of H3K27ac. In parallel, binds to chromatin that lacks histone H3 acetylation at 'Lys-27' (H3K27ac) and recruits EP300 and CREBBP to promote acetylation of histone H3 at 'Lys-27' at new sites (PubMed:26951377). Involved in transcriptional regulation of numerous genes, primarily as transcriptional activator, but mediates also repression of a set of target genes (PubMed:17984056, PubMed:27378237, PubMed:26951377, PubMed:28459457, PubMed:28459454, PubMed:29618456, PubMed:30540931, PubMed:29572508). Promotes expression of ZSCAN4 and KDM4E, two proteins with essential roles during early embryogenesis (PubMed:27378237, PubMed:26951377, PubMed:28459457, PubMed:29618456). Heterologous expression in cultured embryonic stem cells mediates also transcription of HERVL retrotransposons and transcripts derived from ACRO1 and HSATII satellite repeats (PubMed:28459457). May activate expression of PITX1 (PubMed:17984056). May regulate microRNA (miRNA) expression (PubMed:24145033). Inappropriate expression can inhibit myogenesis and promote apoptosis (PubMed:26951377, PubMed:28935672, PubMed:29618456). {PubMed:17984056, PubMed:24145033, PubMed:26951377, PubMed:27378237, PubMed:28459454, PubMed:28459457, PubMed:28935672, PubMed:29572508, PubMed:29618456, PubMed:30315230, PubMed:30540931}.; [Isoform 2]: Probably inactive as a transcriptional activator, due to the absence of the C-terminal region that is important for transcriptional activation. Can inhibit transcriptional activation mediated by isoform 1. Heterologous expression of isoform 2 has no deleterious effect on cell survival. {PubMed:29618456}.
Research Areas Neuroscience
Background Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) is caused by the deletion of a subset of D4Z4 macro-satellite repeats on chromosome 4. Each repeat contains a retrogene encoding the double-homeobox factor DUX4. DUX4 expression is epi- genetically suppressed in differentiated tissues, and the residual DUX4 transcripts are spliced to remove the carboxyterminal domain that has been associated with cell toxicity. In FSHD individuals, the expression of the full-length DUX4 transcript is not completely suppressed in skeletal muscle and possibly other differentiated tissues.
Application Images



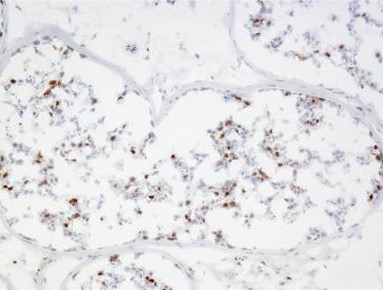
Description Frozen sections of human testis stained with P2B1.

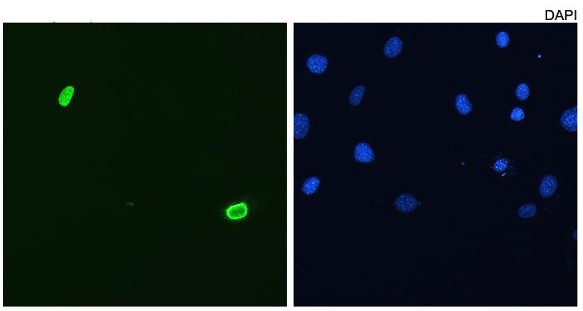
Description C2C12 myoblasts transfected with pCS2+DUX4 stained with P2B1. Counterstained with DAPI for nuclei.
Handling
Storage This antibody is stable for at least one (1) year at -20°C.
Dilution Instructions Dilute in PBS or medium that is identical to that used in the assay system.
Application Instructions ImmunohistochemistryImmunofluorescenceSee reference below for procedural details.
Enduser should determine optimal concentrations for their applications.
Enduser should determine optimal concentrations for their applications.
References & Data Sheet
References Snider L et al 2010 PLoS Genetics 6: 1-14.
Data Sheet  Download PDF Data Sheet
Download PDF Data Sheet
 Download PDF Data Sheet
Download PDF Data Sheet